Antibiotic Quality Assessment in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia at General Hospital in Bali
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v10i1.7592Keywords:
community-acquired pneumonia, Gyssens, Length of StayAbstract
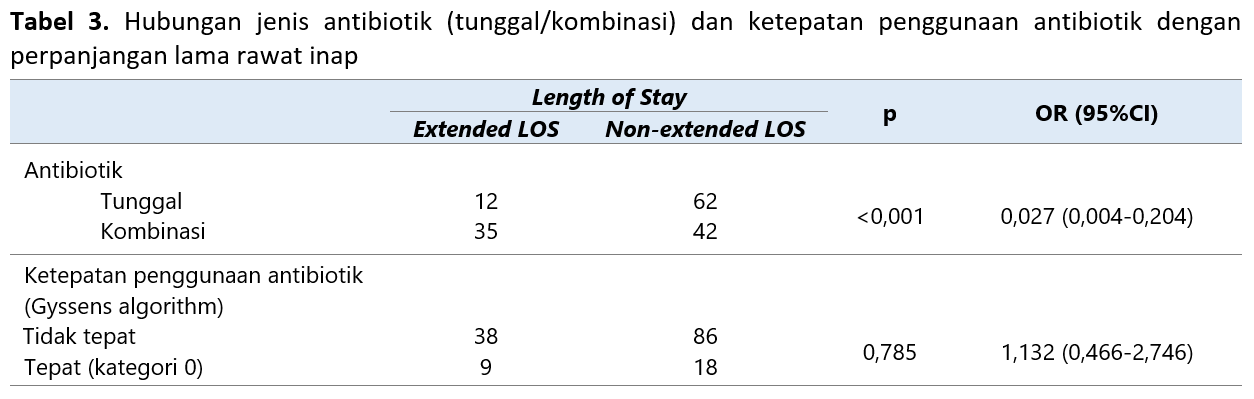
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is an infectious disease with high morbidity and mortality rates. Antibiotics are essential therapies for bacterial CAP. The use of antibiotics is a critical point in CAP treatment. Inappropriate use of antibiotics leads to antibiotic resistance. The study aimed to evaluate the proper use of antibiotics in CAP patients and identify the relationship between the appropriate use of antibiotics and the use of single/combined antibiotics with prolonged length of stay. This study was a cross-sectional study with retrospective data collection at a general hospital in Bali. Evaluation of the proper use of antibiotics was done using the Gyssens algorithm. The relationship between the appropriate use of antibiotics and the type of antibiotic (single/combined) with the length of stay was carried out using the Chi-square test with a 95% confidence interval. There were 151 CAP patients as samples in this study consisting of 55.63% men and 44.37% women with a median age of 60 years (18-89). The appropriate use of antibiotics was 17.88%, while 82.18% of the total antibiotic use was inappropriate. The Inappropriate use of antibiotics in category IIA (incorrect dosage) is 3.97%, category IIIB (inappropriate interval) is 4.64%, category IVC (cheaper alternative antibiotics were available) is 41.72%, and category V (no indication) is 37.79%. There is no significant relationship between the appropriate use of antibiotics and prolonged LOS [p>0.05; OR: 1.132 (CI: 0.466-2.746)] however the use of antibiotics (single or in combination) significantly affects the prolonged LOS [p<0.05; OR: 0.027 (CI: 0.004-0.204)].
References
Puzz L, Plauche EA, Cretella DA, Harrison VA, Wingler MJB. Evaluation of a Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia Antimicrobial Stewardship Intervention at an Academic Medical Center. Antibiotics. 2023;12(4):780.
Fally M, Israelsen S, Benfield T, Tarp B, Ravn P. Time to antibiotic administration and patient outcomes in community-acquired pneumonia: results from a prospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021;27(3):406-412.
Lokida D, Farida H, Triasih R, et al. Epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia among hospitalised children in Indonesia: a multicentre, prospective study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):e057957.
Bielicki JA, Stöhr W, Barratt S, et al. Effect of amoxicillin dose and treatment duration on the need for antibiotic re-treatment in children with community-acquired pneumonia: the CAP-IT randomized clinical trial. Jama. 2021;326(17):1713-1724.
Limato R, Lazarus G, Dernison P, et al. Optimizing antibiotic use in Indonesia: A systematic review and evidence synthesis to inform opportunities for intervention. Lancet Reg Heal Asia. 2022.
Chandrasekhar D, Manaparambil H, Parambil JC. Outcome assessment of intervention on appropriateness of antibiotic use among geriatric patients: A prospective interventional study from a tertiary care referral hospital. Clin Epidemiol Glob Heal. 2019;7(4):536-541.
Nelwan EJ, Guterres H, Pasaribu AI, Shakinah S, Limato R, Widodo D. The Comparison of Point Prevalence Survey (PPS) and Gyssens Flowchart Approach on Antimicrobial Use Surveillance in Indonesian National Referral Hospital. Acta Med Indones. 2021;53(4):505-511.
Park SY, Kim YC, Lee R, Kim B, Moon SM, Kim H Bin. Current Status and Prospect of Qualitative Assessment of Antibiotics Prescriptions. Infect Chemother. 2022;54(4):599.
Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):e45-e67.
Rivero-Calle I, Pardo-Seco J, Aldaz P, et al. Incidence and risk factor prevalence of community-acquired pneumonia in adults in primary care in Spain (NEUMO-ES-RISK project). BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16(1):1-8.
Shen L, Jhund PS, Anand IS, et al. Incidence and outcomes of pneumonia in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(16):1961-1973.
Nathala P, Sarai S, Salunkhe V, Tella MA, Furmanek SP, Arnold FW. Comparing Outcomes for Community-Acquired Pneumonia Between Females and Males: Results from the University of Louisville Pneumonia Study. Univ Louisv J Respir Infect. 2022;6(1):19.
Torres A, Peetermans WE, Viegi G, Blasi F. Risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia in adults in Europe: a literature review. Thorax. 2013;68(11):1057-1065.
Rumende CM, Chen LK, Karuniawati A, et al. Hubungan antara ketepatan pemberian antibiotik berdasarkan alur Gyssens dengan perbaikan klinis pasien pada pneumonia komunitas. J Penyakit Dalam Indones Vol. 2019;6(2).
Widiyastuti A, Kumala S, Utami H, Pratama A. Hubungan Rasionalitas Penggunaan Antibiotik terhadap Luaran Klinis Pasien Pneumonia Komunitas Rawat Inap. J Kesehat. 2023;14(1):109-116.
Muhlis M, Novalinda R. Hubungan Ketepatan Peresepan Antibiotika Berdasarkan Metode Gyssens Terhadap Perbaikan Klinis Pada Pneumonia Komunitas Di RS Swasta Kota Yogyakarta. PRAEPARANDI J Farm dan Sains. 2022;6(1):1-19.
Wikantiananda T, Tjahjadi AI, Sudjud RW. Antibiotic Utilization Pattern in the Intensive Care Unit of Tertiary Hospital in West Java, Indonesia. Int J Integr Heal Sci. 2019;7(2):81-87. doi:10.15850/ijihs.v7n2.1633
Choi S-H, Cesar A, Snow TAC, Saleem N, Arulkumaran N, Singer M. Respiratory fluoroquinolone monotherapy vs. β-Lactam plus macrolide combination therapy for hospitalized adults with community-acquired pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2023;62(3):106905. doi:10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2023.106905
Al Muqati H, Al Turaiki A, Al Dhahri F, Al Enazi H, Althemery A. Superinfection rate among the patients treated with carbapenem versus piperacillin/tazobactam: Retrospective observational study. J Infect Public Health. 2021;14(3):306-310.
Torres A, Chalmers JD, Dela Cruz CS, et al. Challenges in severe community-acquired pneumonia: a point-of-view review. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45:159-171.
Guerra D, Vidal P, Paccoud O, et al. Dual beta-Lactam treatment: Pros and cons. Porto Biomed J. 2022;7(5).
Jiao Y, Moya B, Chen M-J, et al. Comparable efficacy and better safety of double β-Lactam combination therapy versus β‑Lactam plus aminoglycoside in gram-negative bacteria in randomized, controlled trials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(7):10-1128.
Cunha BA. Antibiotic Essentials Fourteenth Edition. India: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Pvt. Ltd.; 2015.
Raymond B. Five rules for resistance management in the antibiotic apocalypse, a road map for integrated microbial management. Evol Appl. 2019;12(6):1079-1091.
Schmid A, Wolfensberger A, Nemeth J, Schreiber PW, Sax H, Kuster SP. Monotherapy versus combination therapy for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15290.
van den Bosch CMA, Hulscher MEJL, Akkermans RP, Wille J, Geerlings SE, Prins JM. Appropriate antibiotic use reduces length of hospital stay. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(3):923-932.
Fésüs A, Benkő R, Matuz M, et al. Impact of Guideline Adherence on Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) in Hungary: A Retrospective Observational Study. Antibiotics. 2022;11(4):468.
Pangeran SAB, Manggau MA, Djaharuddin I. Evaluasi Penggunaan Terapi Antibiotik Empiris Terhadap Luaran Klinis Pasien Pneumonia Komunitas Rawat Inap. Maj Farm dan Farmakol. 2022;26(1):19-25.
Tambun SH, Puspitasari I, Laksanawati IS. Evaluasi luaran klinis terapi antibiotik pada pasien community acquired pneumonia anak rawat inap. J Manaj Dan Pelayanan Farm (Journal Manag Pharm Pract. 2019;9(3):213-224.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Herleeyana Meriyani, Dwi Arymbhi Sanjaya, Rr. Asih Juanita, Nyoman Budiartha Siada

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





















