Factors Associated with Length of Stay of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Patients at a Regional General Hospital in Bali
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v11i1.9852Keywords:
DHF, ringer lactate, length of stayAbstract
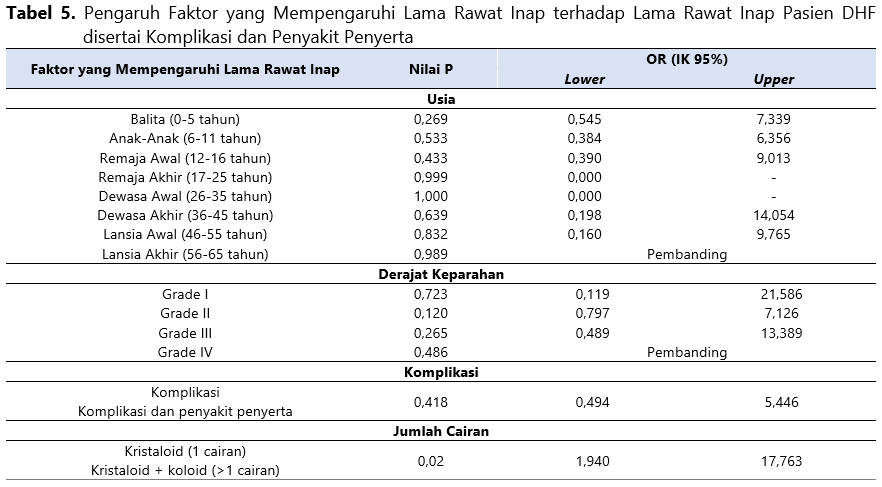
The World Health Organization (WHO) reported one to five million dengue infections from 2020 to 2022. According to Indonesian Health Profile data in 2020, the province of Bali had the highest Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) Incidence Rate (IR), 273.1 morbidity, and a Case Fatality Rate (CFR) of 0.2%. The longer the patient's stay, the greater the costs are incurred for hospital treatment. Therefore, this study aims to analyze the factors influencing the length of stay of DHF patients with complications and comorbidities. This study was an observational study. Medical record data of DHF patients with complications and comorbidities were collected using a retrospective technique from January 2020 to December 2020 during hospitalization at a regional public hospital in Bali. The independent variables in this study include age, the severity of DHF, complications and comorbidities, and the amount of fluid therapy patients use during hospitalization. The dependent variable in this study is the patient's length of stay. The relationship between the independent and dependent variables was analyzed using logistic regression with a significance level set at p<0.05. There were 115 hospitalized DHF patients with complications and comorbidities, consisting of 52% males and 48% females. Most patients were in the age range of 6-11 years (43%). Based on the analysis that has been carried out, there is a factor that is significantly related to the length of stay of DHF patients, namely the use of the amount of fluid therapy (p=0.02). The findings of this study support the evaluation of DHF therapy, particularly in selecting the type and volume of fluids.
References
World Health Organization. Global Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases 2024: Executive Summary.; 2024. doi:10.2471/b09040
Kemenkes RI. Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2020. Vol 48.; 2021. doi:10.1524/itit.2006.48.1.6
Kemenkes RI. Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2021.; 2022.
Cahyani S, Rizkianti T, Susantiningsih T. Hubungan Jumlah Trombosit , Nilai Hematokrit dan Rasio Neutrofil-Limfosit Terhadap Lama Rawat Inap Pasien DBD Anak di RSUD Budhi Asih Bulan Januari – September Tahun2019. Semin Nas Ris Kedokt 2020. 2020;1(1):49-59.
Tursinawati Y, Ramaningrum G, Aprilia I. Laboratory Finding and Clinical Manifestation Affecting the Length of Stay of Hospitalization on Children With Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever. Pros Semin Nas Int. 2017;1(1):130-135.
Arianti MD, Prijambodo J, Wujoso H. Relationships between Age , Sex , Laboratory Parameter , and Length of Stay in Patients with Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever. J Epidemiol Public Heal. 2019;4(4):307-313.
Syam I, Khair H. Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Lama Hari Rawat Inap Pada Pasien DBD Di RSUD Barru. Info Kesehat. 2019;9(2):158-163.
Rahmawati A, Perwitasari DA, Kurniawan NU. Efektivitas Pemberian Terapi Cairan Inisial Dibandingkan Terapi Cairan Standar WHO terhadap Lama Perawatan pada Pasien Demam Berdarah di Bangsal Anak Rumah Sakit PKU Muhammadiyah Bantul. Indones J Clin Pharm. 2019;8(2):91. doi:10.15416/ijcp.2019.8.2.91
Kunti DPSA, Suryana K. Factors associated with prolonged length of stay in dengue hemorrhagic fever patients at Wangaya Hospital, Denpasar, Bali. Int J Adv Med. 2024;11(4):328-332. doi:10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20241624
Hikmawati I, Patima S. Cross Section a Study: The Relationship Between Comorbidities and Hematocrit with the Hospitalization of Patients of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF). Adv Sci Lett. 2018;24(1):112-115. doi:10.1166/asl.2018.11934
Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran Tata Laksana Infeksi Dengue Anak dan Remaja. Pedoman Nas pelayanan Kedokt. Published online 2021:1-67.
Kemenkes RI. Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran Tata Laksana Infeksi Dengue Pada Dewasa. Vol 8.; 2020.
Ayu Islammia D putri, Rumana NA, Indawati L, Dewi DR. Karakteristik Pasien Demam Berdarah Dengue Rawat Inap di Rumah Sakit Umum UKI Tahun 2020. SEHATMAS J Ilm Kesehat Masy. 2022;1(1):60-70. doi:10.55123/sehatmas.v1i1.37
Ningrum DM, Septiana E, Permana DAS, Wahida A. Kajian Pengobatan Dengue Haemoragic Fever (DHF) di Rumah Sakit Pendidikan Universitas Mataram. J Ilmu Kefarmasian. 2023;4(1):1-6.
Aamir M, Masood G, Aamir W, Rasheed A, Ejaz A, Syed S. Gender difference in patients with dengue fever admitted in a teaching hospital, Lahore. Pakistan J Med Heal Sci. 2014;8(1):12-15.
Halimah Amini N, Hartoyo E. Hubungan Hematokrit Dan Jumlah Trombosit Terhadap Lama Rawat Inap Pasien Dbd Anak Di Rsud Ulin Banjarmasin. Homeostasi. 2019;2:407-416.
Sari RN, Natalia D, Parinding JT. Hubungan Lama Demam dengan Hasil Pemeriksaan Antigen Nonstruktural 1 Dengue pada Pasien Demam Berdarah Dengue di RSUD Sultan Syarif Mohamad Alkadrie Tahun 2018. J BiomedikJBM. 2020;12(3):153. doi:10.35790/jbm.12.3.2020.31186
Perdani AL, Hendra A, Mutiar A, Heriani W. Identifying clinical features of fluid status among children with suspect dengue in Indonesia. Malahayati Int J Nurs Heal Sci. 2021;4(1):74-78.
Martini M, Efriana S, Fajarini R, et al. Genotype Variants Of Dengue Virus On Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (Dhf) Suspect: Cross Sectional Study In Health Facilities In Semarang City, Indonesia. Eur J Mol Clin Med. 2020;7(8):730-740.
Tristianti VR, Daten Beyeng RT. The Correlation Between Nutritional Status With Severity of Dengue Infection in Pediatric Patients. Int J Healthc Sci. 2022;10(2):14-18.
Muller DA, Depelsenaire ACI, Young PR. Clinical and Laboratory Diagnosis of Dengue Virus Infection. J Infect Dis. 2017;215(suppl_2):S89-S95. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiw649
Hussain R, Hashir MM, Awan Z, Abid N. Myocarditis in dengue fever - A retrospective review from a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. Pakistan J Med Heal Sci. 2017;11(2):707-710.
Andriati R, Trisutrisno D. Pengaruh Resusitasi cairan Terhadap Status Hemodinamik Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) pada Pasien Syok Hipovolemik di IGD RSUD Balaraja. Med Surg Concerns. 2021;1(1):1-13.
Munawaroh U, Nurmainah, Untari EK. Gambaran Penggunaan Antibiotik Pada Pasien Anak yang Menderita Demam Berdarah Dengue (DBD) di Instalasi Rawat Inap RSUD Sultan Syarif Mohammad Alkadrie Pontianak Tahun 2017. J Mhs Farm Fak Kedokt UNTAN. 2019;4(1):1-15.
Vimal S, Vishwanathan V, Dharwadker A. Dengue and Typhoid co-infection Study. J Med Pharm Allied Sci. 2022;11(2):4542-4546. doi:10.55522/jmpas.V11I2.2347
Chauhan S, Sharma S, . S, Singh P. Concurrent dengue and typhoid infection: study from a tertiary care centre in Muzaffarnagar, India. Int J Res Med Sci. 2019;7(5):1615. doi:10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20191646
Nuevo FR, Vennari M, Agrò FE. How to Maintain and Restore Fluid Balance: Crystalloids.; 2013. doi:10.1007/978-88-470-2661-2_3
Liamis G, Filippatos TD, Elisaf MS. Correction of hypovolemia with crystalloid fluids: Individualizing infusion therapy. Postgrad Med. 2015;127(4):405-412. doi:10.1080/00325481.2015.1029421
Singh S, Kerndt CC, Davis D. Ringer’s Lactate. React Wkly. 2022;NA;(1365):40. doi:10.2165/00128415-201113650-00153
Nopianto H. Faktor-Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Terhadap Lama Rawat Inap Pada Pasien Demam Berdarah Dengue Di RSUP Dr Kariadi Semarang.; 2012.
Perwira I. Faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi lama rawat inap pada pasien yang terinfeksi virus dengue di RSUP Persahabatan , Jakarta Timur. Tesis Univ Indones. Published online 2011:20238015.
Munawwarah BAA, Perwitasari DA, Kurniawan NU. Efektivitas Cairan Kristaloid dan Koloid Pasien Demam Berdarah Anak di Rumah Sakit PKU Muhammadiyah Bantul. J Farm dan Ilmu Kefarmasian Indones. 2019;5(1):20. doi:10.20473/jfiki.v5i12018.20-29
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nyoman Budiartha Siada, Rr Asih Juanita

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





















