Antibiotic Consumption and Its Influence on Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Resistance: A Five-Year Ecological Study in a Regional Hospital
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v11i2.11156Keywords:
cross-resistance, DDD/100 bed-days, Eschericia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, meropenemAbstract
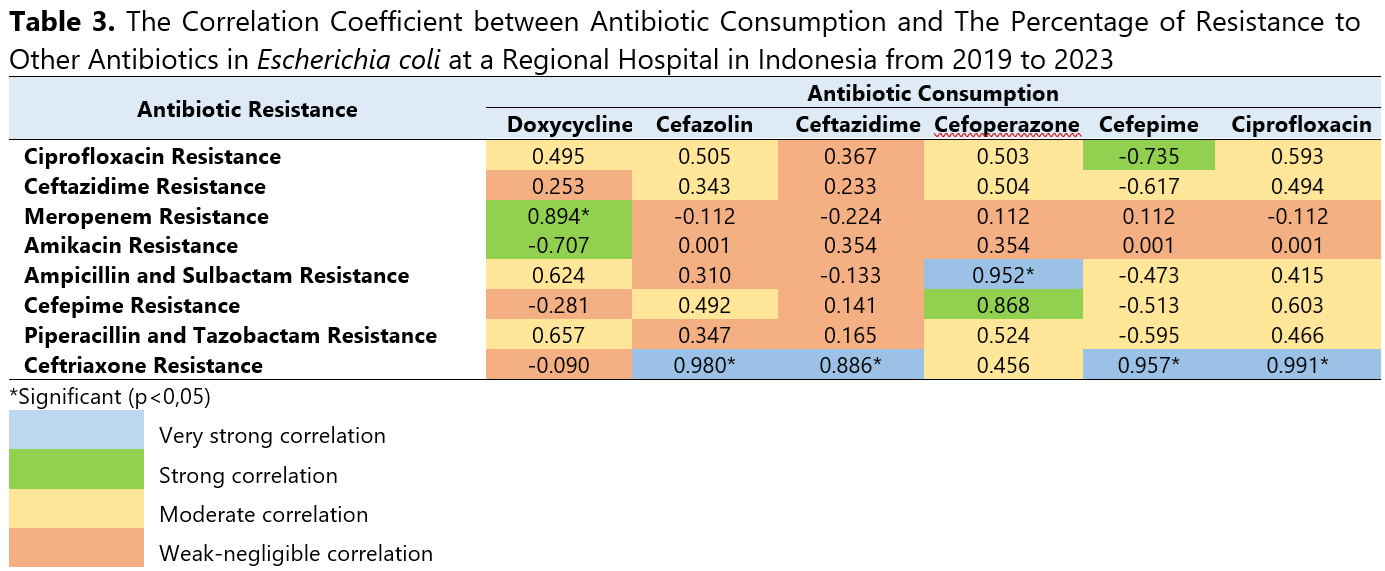
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global health threat, partly driven by high antibiotic consumption. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified critical-priority bacteria, including Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, due to their increasing resistance to multiple antibiotics. This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between antibiotic consumption and resistance rates in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. This ecological study was conducted at a Regional Hospital in Indonesia based on retrospective inpatient data from January 2019 to December 2023. The population in this study is all data on systemic antibiotic consumption based on the J01 category of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical/Defined Daily Dose (ATC/DDD) classification system and antibiogram from inpatient databases. Pearson and Spearman’s rank correlation analyses were performed to examine the associations between systemic antibiotic consumption levels and the percentage of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae resistance to other antibiotics. The most frequently used antibiotics were cefixime (305.664 DDD/100 bed-days), levofloxacin (139.552 DDD/100 bed-days), and ceftriaxone (109.805 DDD/100 bed-days). A strong and statistically significant correlation was observed between doxycycline consumption and Escherichia coli resistance to meropenem (r=0.894; p=0.041). Moreover, consumption levels of cefazolin, ceftazidime, cefepime, and ciprofloxacin were correlated with Escherichia coli resistance to ceftriaxone (p<0.05), while cefoperazone use demonstrated a very strong and statistically significant correlation with Escherichia coli resistance to ampicillin-sulbactam (r=0.952; p=0.012). Conversely, no significant correlation was found between antibiotic consumption and resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, suggesting that alternative factors such as intrinsic resistance mechanisms, mobile genetic elements, and environmental reservoirs may influence resistance development.
References
1. Bassetti S, Tschudin-Sutter S, Egli A, Osthoff M. Optimizing antibiotic therapies to reduce the risk of bacterial resistance. Eur J Intern Med. 2022;99(October 2021):7-12. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2022.01.029
2. Sofro MAU, Suryoputro A, Anies A. Systematic Review: Implementasi dan Dampak Antimicrobial Stewardship Program pada Fasilitas Kesehatan di Berbagai Negara. J Ilmu Kesehat Masy. 2022;11(06):544-564. doi:10.33221/jikm.v11i06.1615
3. Gajdács M, Urbán E, Stájer A, Baráth Z. Antimicrobial resistance in the context of the sustainable development goals: A brief review. Eur J Investig Heal Psychol Educ. 2021;11(1):71-82. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11010006
4. Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, et al. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(12):1057-1098. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9
5. WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS) Report.; 2017. doi:ISBN 978-92-4-151344-9
6. Macvane SH. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Intensive Care Unit. J Intensive Care Med. 2017;32(1):25-37. doi:10.1177/0885066615619895
7. Ziółkowski G, Pawłowska I, Krawczyk L, Wojkowska-Mach J. Antibiotic consumption versus the prevalence of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Clostridium difficile infections at an ICU from 2014–2015. J Infect Public Health. 2018;11(5):626-630. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2018.02.003
8. Trejnowska E, Deptuła A, Tarczyńska-Słomian M, et al. Surveillance of Antibiotic Prescribing in Intensive Care Units in Poland. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2018;2018. doi:10.1155/2018/5670238
9. Mancuso G, Midiri A, Gerace E, Biondo C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens. 2021;10(10). doi:10.3390/pathogens10101310
10. WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization; 2024.
11. Arato V, Raso MM, Gasperini G, Berlanda Scorza F, Micoli F. Prophylaxis and Treatment against Klebsiella pneumoniae: Current Insights on This Emerging Anti-Microbial Resistant Global Threat. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):4042. doi:10.3390/ijms22084042
12. Pérez-Lazo G, Abarca-Salazar S, Lovón R, et al. Antibiotic Consumption and Its Relationship with Bacterial Resistance Profiles in ESKAPE Pathogens in a Peruvian Hospital. Antibiotics. 2021;10(10). doi:10.3390/antibiotics10101221
13. Tan SY, Khan RA, Khalid KE, Chong CW. Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug ‑ resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital : a 3 ‑ year observational study. Sci Rep. Published online 2022:1-9. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-07142-2
14. Navon-Venezia S, Kondratyeva K, Carattoli A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: a major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41(3):252-275. doi:10.1093/femsre/fux013
15. Bethke JH, Ma HR, Tsoi R, Cheng L, Xiao M, You L. Vertical and Horizontal Gene Transfer Tradeoffs Direct Plasmid Fitness. Mol Syst Biol. 2022;19(2):1-10. doi:10.15252/msb.202211300
16. Truong R, Tang V, Grennan T, Tan DHS. A Systematic Review of the Impacts of Oral Tetracycline Class Antibiotics on Antimicrobial Resistance in Normal Human Flora. JAC-Antimicrobial Resist. 2022;4(1):1-12. doi:10.1093/jacamr/dlac009
17. Tao H, Wang J, Li L, Zhang HZ, Chen MP, Li L. Incidence and Antimicrobial Sensitivity Profiles of Normal Conjunctiva Bacterial Flora in the Central Area of China: A Hospital-Based Study. Front Physiol. 2017;8(363):1-6. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00363
18. Anggraini D, Endraputra PN, Sarassari R, et al. Antibiotic Resistance Report from The Surveillance of Indonesia Network on Antimicrobial Resistance (SINAR) 2023. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2024;39:20. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2024.10.061
19. Amaha ND, Weldemariam DG, Berhe YH. Antibiotic consumption study in two hospitals in Asmara from 2014 to 2018 using WHO’s defined daily dose (DDD) methodology. PLoS One. 2020;15(7):e0233275. doi:doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233275
20. Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(5):1763-1768.
21. Wushouer H, Zhou Y, Zhang W, et al. Inpatient Antibacterial Use Trends and Patterns, China, 2013–2021. Bull World Health Organ. 2023;101(4):248-261B. doi:10.2471/BLT.22.288862
22. Aierken A, Zhu X, Wang N, et al. Measuring Temporal Trends and Patterns of Inpatient Antibiotic Use in Northwest China’s Hospitals: Data from the Center for Antibacterial Surveillance, 2012–2022. Antibiotics. 2024;13(8):2012-2022. doi:10.3390/antibiotics13080732
23. Azyenela L, Tobat SR, Selvia L. Evaluasi Penggunaan Antibiotik di Instalasi Rawat Inap Bedah RSUD M. Natsir Kota Solok Tahun 2020. J Mandala Pharmacon Indones. 2022;8(1):1-10. doi:10.35311/jmpi.v8i1.123
24. Latifah N, Andayani TM, Ikawati Z. Perbandingan Efektivitas Cefazolin dan Ceftriaxone Sebagai Antibiotik Profilaksis Bedah Ortopedi Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) Fraktur Tertutup. JPSCR J Pharm Sci Clin Res. 2021;3:307-317. doi:10.20961/jpscr.v6i3.52630
25. Kizito M, Owachi D, Lule F, et al. Antibiotic consumption and utilization at a large tertiary care level hospital in Uganda: A point prevalence survey. PLoS One. 2025;20(1):e0313587. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313587
26. Hanifah S, Melyani I, Madalena L. Evaluasi Penggunaan Antibiotik dengan Metode ATC/DDD DAN DU90% pada Pasien Rawat Inap Kelompok Staff Medik Penyakit Dalam di Salah Satu Rumah Sakit Swasta di Kota Bandung. Farmaka. 2022;20(1):21-26.
27. Podder V, Patel P, Sadiq NM. Levofloxacin. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
28. Zanichelli V, Sharland M, Cappello B, et al. The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) antibiotic book and prevention of antimicrobial resistance. Bull World Health Organ. 2023;101(4):290. doi:https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.22.288614
29. Ruekit S, Srijan A, Serichantalergs O, et al. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant ESKAPEE pathogens from clinical samples in Chonburi, Thailand (2017–2018). BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):695. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-022-07678-8
30. Wang S, Zhao S, Zhou Y, Jin S, Ye T, Pan X. Antibiotic resistance spectrum of E. coli strains from different samples and age-grouped patients: a 10-year retrospective study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(4):e067490. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067490
31. Naqid IA, Hussein NR, Balatay AA, Saeed KA, Ahmed HA. The antimicrobial resistance pattern of Klebsiella pneumonia isolated from the clinical specimens in Duhok City in Kurdistan Region of Iraq. J Kermanshah Univ Med Sci. 2020;24(2):e106135. doi:10.5812/jkums.106135
32. Do Tran H, Nguyen NC, Nguyen HD, et al. The situation of antibiotic resistance in klebsiella pneumoniae and carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae in Vietnam: A cross-sectional study. J Heal Sci Med Res. 2023;42(1):2023964. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.31584/jhsmr.2023964
33. Eiamphungporn W, Schaduangrat N, Malik AA, Nantasenamat C. Tackling the antibiotic resistance caused by class A β-lactamases through the use of β-lactamase inhibitory protein. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2222.
34. Afsharikhah S, Ghanbarpour R, Mohseni P, Adib N, Bagheri M, Jajarmi M. High prevalence of β-lactam and fluoroquinolone resistance in various phylotypes of Escherichia coli isolates from urinary tract infections in Jiroft city, Iran. BMC Microbiol. 2023;23(1):114. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-023-02860-7
35. Li Y, Kumar S, Zhang L, Wu H, Wu H. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Open Med. 2023;18(1). doi:10.1515/med-2023-0707
36. Huy TXN. Overcoming Klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic resistance: new insights into mechanisms and drug discovery. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2024;13(1). doi:10.1186/s43088-024-00470-4
37. T Das A, Tenenbaum L, Berkhout B. Tet-on systems for doxycycline-inducible gene expression. Curr Gene Ther. 2016;16(3):156-167.
38. Møller TSB, Overgaard M, Nielsen SS, et al. Relation between tetR and tetA expression in tetracycline resistant Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2016;16(1):39.
39. Poirel L, Madec JY, Lupo A, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Sepsis. Microbiol Spectr Am Soc Microbiol. 2018;6(4):1-27. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.ARBA-0026-2017
40. Huang J, Lv C, Li M, et al. Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli Exhibit Diverse Spatiotemporal Epidemiological Characteristics Across the Globe. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):1-13. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-05745-7
41. Zou H, Jia X, Liu H, Li S, Wu X, Huang S. Emergence of NDM-5-Producing Escherichia coli in a Teaching Hospital in Chongqing, China: IncF-Type Plasmids May Contribute to the Prevalence of blaNDM–5. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1-9. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.00334
42. Walker MM, Roberts JA, Rogers BA, Harris PNA, Sime FB. Current and Emerging Treatment Options for Multidrug Resistant Escherichia coli Urosepsis: A Review. Antibiotics. 2022;11:1-20. doi:10.3390/antibiotics11121821
43. Bevan ER, Jones AM, Hawkey PM. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(8):2145-2155. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx146
44. Pratama AS, Djide MN, Massi MN. Identifikasi Genotip CTX-M pada Escherichia coli Penghasil Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase (ESBL) yang Resisten pada Cephalosporin Generasi III di RSUP Wahidin Sudirohusodo Makasar. Maj Farm dan Farmakol. 2019;23(1):5-9. doi:10.20956/mff.v23i1.6458
45. Hayer SS, Lim S, Hong S, et al. Genetic determinants of resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone in Escherichia coli isolated from diseased pigs in the United States. Msphere. 2020;5(5):10-1128. doi:10.1128/msphere.00990-20
46. Nirwati H, Sinanjung K, Fahrunissa F, et al. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from clinical samples in a tertiary care hospital, Klaten, Indonesia. BMC Proc. 2019;13(S11):20. doi:10.1186/s12919-019-0176-7
47. Braun HG, Perera SR, Tremblay YDN, Thomassin J lee. Antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae : an overview of common mechanisms and a current Canadian perspective. 2024;22:1-22.
48. Meriyani H, Sanjaya DA, Juanita RA, Siada NB. Kajian Literatur: Study Design Dalam Farmakoepidemiologi Untuk Mengetahui Resistensi Bakteri Terhadap Antibiotik. JPSCR J Pharm Sci Clin Res. 2023;8(1):13-31. doi:10.20961/jpscr.v8i1.61651
49. Liu J, Zhang S, Huang S, et al. Rationality of time-dependent antimicrobial use in intensive care units in China: a nationwide cross-sectional survey. Front Med. 2021;8:584813. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.584813
50. WHO. Guidelines for ATC Classification and DDD Assignment 2023. 26th ed. WHO; 2023.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dwi Arymbhi Sanjaya, Herleeyana Meriyani, Rr. Asih Juanita, Nyoman Budiartha Siada, Yudistira Mahaputra, Made Gek Adisti Kamalia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





















