Analysis of the Relationship between Hypertension Knowledge with Medication Compliance and Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v9i1.5470Keywords:
Blood pressure control, hypertension, knowledge, Treatment-complianceAbstract
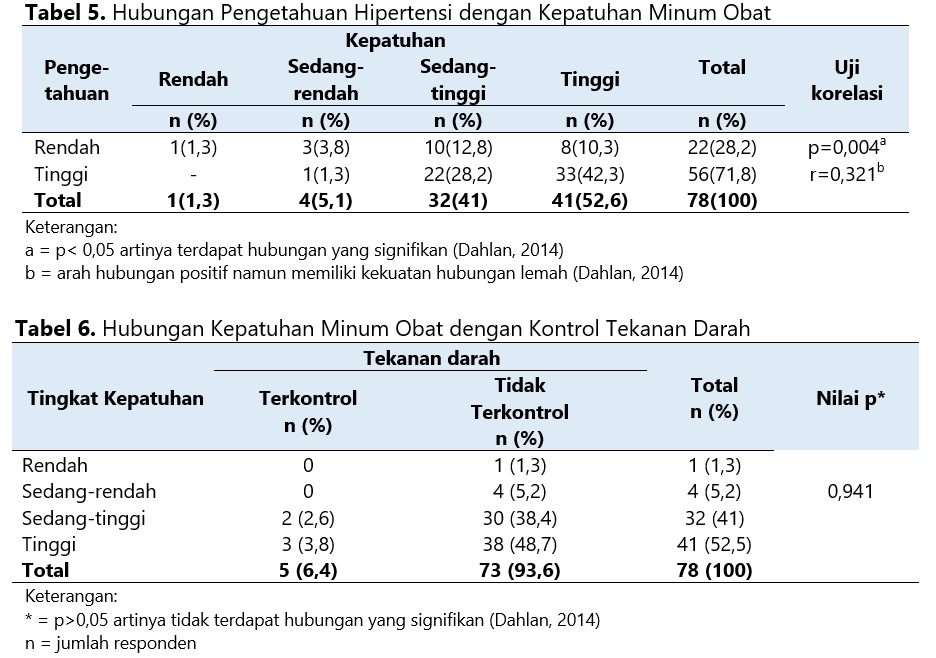
Hypertension is a chronic disease with a high mortality rate, and patient adherence to treatment is still low. Low patient adherence can be caused by several factors, including patient knowledge related to hypertension. In addition, medication adherence is a factor that can affect blood pressure control. This study aimed to analyze the relationship between knowledge, adherence, and blood pressure control in hypertensive patients. This research was conducted at Tk.II Udayana Hospital Denpasar with data collection time, namely February-April 2022. The research design was carried out cross-sectionally using a validated questionnaire. The level of patient knowledge was measured using the Hypertension Knowledge Level Scale (HK-LS) questionnaire, and the level of patient compliance was measured using the Probabilistic Medication Adherence Scale (ProMAS) questionnaire. The patient's blood pressure data has been seen through the patient's medical record in the past three months. The sampling technique in this study used a nonprobability sampling technique with a consecutive sampling approach. The data analysis used to determine the relationship between hypertension knowledge and adherence to taking medication is the Pearson correlation test. Differences in blood pressure control at various levels of adherence were tested with the Kruskal-Wallis test. The results of the analysis of 78 respondents showed that there was a significant relationship between knowledge and medication adherence (p=0.004; r=0.321). For drinking compliance with blood pressure control, there was no significant difference in blood pressure control values at various levels of drinking adherence (p=0.941). Thus knowledge related to hypertension affects medication adherence. However, various factors other than medication adherence are needed to produce reasonable blood pressure control.
References
Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Published online 2020:24.
Maulidina F. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kejadian Hipertensi di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Jati Luhur Bekasi Tahun 2018. ARKESMAS Arsip Kesehat Masy. 2019;4(1):149-155. doi:10.22236/arkesmas.v4i1.3141
Kartika M, Subakir S, Mirsiyanto E. Faktor-Faktor Risiko Yang Berhubungan Dengan Hipertensi Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Rawang Kota Sungai Penuh Tahun 2020. J Kesmas Jambi. 2021;5(1):1-9. doi:10.22437/jkmj.v5i1.12396
WHO. World Hypertension Day 2019. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2019/05/17/default-calendar/world-hypertension-day-2019. Published May 17, 2019.
Tim Riset Kesehatan Dasar 2018 (Indonesia), Indonesia, eds. Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018. Kementerian Kesehatan, Republik Indonesia, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan; 2019.
P2PTM Kemenkes RI. Apa Komplikasi Berbahaya dari Hipertensi? Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. https://p2ptm.kemkes.go.id/infographic-p2ptm/hipertensi-penyakit-jantung-dan-pembuluh-darah/page/5/apa-komplikasi-berbahaya-dari-hipertensi. Published August 7, 2019.
Direktorat Pengendalian PTM. Pedoman Teknis Penemuan dan Tatalaksana Hipertensi. Kementerian Kesehatan, Republik Indonesia, Direktorat Pengendalian Penyakit Tidak Menular; 2013. https://p2ptm.kemkes.go.id/dokumen-ptm/pedoman-teknis-penemuan-dan-tatalaksana-hipertensi
Mathavan J, Pinatih GNI. Gambaran tingkat pengetahuan terhadap hipertensi dan kepatuhan minum obat pada penderita hipertensi di wilayah kerja Puskesmas kintamani I. Intisari Sains Medis. 2017;8(3):176-180. doi:10.15562/ism.v8i3.121
Agustine U, Mbakurawang IN. Kepatuhan Minum Obat pada Penderita Hipertensi yang Berobat ke Balai Pengobatan Yayasan Pelayanan Kasih A dan A Rahmat Waingapu. J Kesehat Primer. 2016;1(2):114-122. doi:https://doi.org/10.5281/jkp.v1i2.74
Listiana D, Effendi S, Saputra YE. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kepatuhan Penderita Hipertensi dalam Menjalani Pengobatan di Puskesmas Karang Dapo Kabupaten Muratara. J Nurs Public Health. 2020;8(1):11-22. doi:10.37676/jnph.v8i1.1005
Pratama GW, Ariastuti NLP. Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Kepatuhan Pengobatan Hipertensi pada Lansia Binaan Puskesmas Klungkung 1. E-J Med Udayana. 2015;4(8). https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eum/article/view/20900
Sarampang YT, Tjitrosantoso HM, Citraningtyas G. Hubungan Pengetahuan Pasien Hipertensi tentang Obat Golongan ACE Inhibitor dengan Kepatuhan Pasien dalam Pelaksanaan Terapi Hipertensi di RSUP Prof Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado. Pharmacon. 2014;3(3):225-229. doi:https://doi.org/10.35799/pha.3.2014.5386
Rusida ER, Adhani R, Panghiyangani R. Pengaruh Tingkat Pengetahuan, Motivasi dan Faktor Obat Terhadap Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pasien Hipertensi di Puskesmas Kota Banjarbaru Tahun 2017. J Pharmascience. 2017;4(2). doi:10.20527/jps.v4i2.5766
Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Bali. Profil Kesehatan Provinsi Bali 2021. Dinas Kesehatan Provinsi Bali; 2022.
Dinas Kesehatan Kota Denpasar. Profil Dinas Kesehatan Kota Denpasar Tahun 2021. Dinas Kesehatan Kota Denpasar; 2022.
Dahlan MS. Besar Sampel Dan Cara Pengambilan Sampel Dalam Penelitian Kedokteran Dan Kesehatan. 5th ed. Salemba Medika; 2010.
Ernawati I, Fandinata SS, Permatasari SN. Translation and Validation of the Indonesian Version of the Hypertension Knowledge-level Scale. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2020;8(E):630-637. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2020.5152
Kleppe M, Lacroix J, Ham J, Midden C. The development of the ProMAS: a Probabilistic Medication Adherence Scale. Patient Prefer Adherence. Published online March 2015:355. doi:10.2147/PPA.S76749
Pratama IPY, Andayani TM, Kristina SA. Knowledge, Adherence and Quality of Life Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Int Res J Pharm. 2019;10:52-55.
Dahlan SM. Statistik Untuk Kedokteran dan Kesehatan: Deskriptif, Bivariat dan Multivariat, Dilengkapi Aplikasi Dengan Menggunakan SPSS. 6th ed. Epidemiologi Indonesia; 2014.
Ayuchecaria N, Khairah SN, Feteriyani R. Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pasien Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Pekauman Banjarmasin. J Insan Farm Indones. 2018;1:234-242.
Pramestutie HR, Silviana N. The Knowledge Level of Hypertension Patients for Drug Therapy in the Primary Health Care of Malang. Indones J Clin Pharm. 2016;5(1):26-34. doi:10.15416/ijcp.2016.5.1.26
Sihombing TFH, Artini IGA. Tingkat Pengetahuan Mengenai Hipertensi dan Pola Kepatuhan Pengobatan pada Penderita Hipertensi yang Berkunjung ke Tenda Tensi Tim Bantuan Medis Janar Dūta Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Udayana. Published online 2017:6.
Rahayu ES, Wahyuni KI, Anindita PR. Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan dengan Kepatuhan Pasien Hipertensi di Rumah Sakit Anwar Medika. J Ilm Farm Farmasyifa. 2021;4(1):87-97. doi:10.29313/jiff.v4i1.6794
Berisa H dame, Dedefo MG. Retraction Notice: non-Adherence Related Factors to Antihypertensive Medications Among Hypertensive Patients on Follow Up at Nedjo General Hospital in West Ethiopia. 2018;11.
Bell K, Twiggs J, Olin BR. Hypertension: The Silent Killer: Updated JNC-8 Guideline Recommendations.
Indriana N, Swandari MTK, Pratiwi Y. Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dengan Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Pasien Hipertensi Di Rumah Sakit X Cilacap. J Ilm JOPHUS J Pharm UMUS. 2021;2(01). doi:10.46772/jophus.v2i01.266
Wahyudi CT, Ratnawati D, Made SA. Pengaruh Demografi, Psikososial, dan Lama Menderita Hipertensi Primer terhadap Kepatuhan Minum Obat Antihipertensi. J JKFT. 2017;2(2):14. doi:10.31000/jkft.v2i1.692
Saepudin, Padmasari S, Hidayanti puri, S. Ningsih E. Kepatuhan Penggunaan Obat pada Pasien Hipertensi di Puskesmas. J Farm Indones. 2013;6:246-253.
Nanurlaili SW, Sudhana IW. Gambaran Kepatuhan Minum Obat dan Peran Serta Keluarga pada Keberhasilan Pengobatan Pasien Hipertensi di Desa Timbrah Kecamatan Karangasem Pada Januari 2014. Published online 2014:6.
Benetos A, Petrovic M, Strandberg T. Hypertension Management in Older and Frail Older Patients. Circ Res. 2019;124:1045-1060.
Ihwatun S, Ginandjar P, Saraswati LD, Udiyono A. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kepatuhan Pengobatan pada Penderita Hipertensi di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Pudakpayung Kota Semarang Tahun 2019. J Kesehat Masy. 2020;8:8.
Mangendai Y, Rompas S, Hamel RS. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kepatuhan Berobat pada Pasien Hipertensi di Puskesmas Ranotana Weru. 2017;5:8.
Wirakhmi IN, Purnawan I. Hubungan Kepatuhan Minum Obat dengan Tekanan Darah pada Penderita Hipertensi. J Ilmu Keperawatan Dan Kebidanan. 2021;12.
Anggara FHD, Prayitno N. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Tekanan Darah di Puskesmas Telaga Murni, Cikarang Barat Tahun 2012. Published online 2013.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jurnal Ilmiah Medicamento

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





















