Evaluation of Dose Appropriateness and Potential Drug Interactions in End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients at a Private Hospital in Denpasar, Bali
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v10i2.9143Keywords:
Chronic Kidney Failure, drug interaction, inappropriate dosage, polypharmacyAbstract
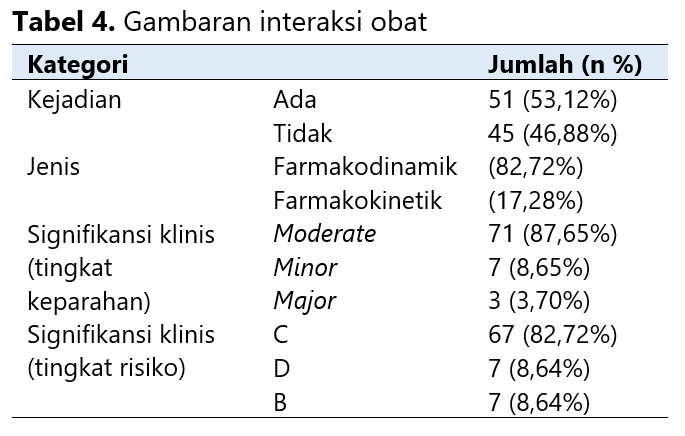
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) is a chronic disease with a high mortality rate and increasing prevalence. Patients often experience complications from hemodialysis (HD) and comorbid conditions, leading to treatment complexity and polypharmacy. These factors increase the risk of drug-related problems, including inappropriate dosing and drug interactions. This study evaluated dose appropriateness and potential drug interactions in ESRD patients. The study employed a cross-sectional design involving 96 ESRD patients at the HD Clinic of a private hospital in Denpasar. Data collection was conducted in May 2021 using a data collection instrument based on medical records and purposive sampling techniques. Inclusion criteria included ESRD patients with or without complications and comorbidities, aged ≥18 years, and receiving ≥3 medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding patients were excluded. Dose adjustments were determined using the Cockcroft-Gault equation and therapeutic guidelines, while drug interactions were assessed using Stockley's Drug Interactions, Drug Interaction Facts, Drug Information Handbook, IBM Micromedex®, and Medscape®. The results showed that most patients were aged 45-59 years (46.88%), male (68.75%), had hypertension complications (42.31%), and had comorbid dyslipidemia (55.56%). Most patients received 5-7 drugs (40.62%), primarily vitamins (18.06%), administered once daily (38.26%) and orally (71.26%). A total of 23 prescriptions (23.96%) required dose adjustment, and 53.12% of prescriptions had potential drug interactions, mainly pharmacodynamic (82.72%), with moderate severity (87.65%) and risk category C (82.72%). Pharmacists' roles in reviewing prescriptions should be enhanced to prevent or minimize drug-related problems.
References
Thurlow JS, Joshi M, Yan G, et al. Global epidemiology of end-stage kidney disease and disparities in kidney replacement therapy. American Journal of Nephrology. 2021;52(2):98-107. doi:10.1159/000514550
Gupta R, Woo K, Yi JA. Epidemiology of end-stage kidney disease. Seminars in Vascular Surgery. 2021;34(1):71-78. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2021.02.010
USRDS. 2021 Annual Data Report Table of Contents Incidence , Prevalence , Patient Characteristics , and Treatment Modalities.; 2021.
Kementrian Kesehatan R. Laporan Nasional RISKESDAS 2018. Published online 2018:1-674.
Wouk N. End-Stage Renal Disease: Medical Management. American Family Physician. 2021;104(5):493-499.
Thenmozhi P. Quality of life of patients undergoing hemodialysis. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2018;11(4):219-223. doi:10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i4.24007
Habas E, Habas A, Elgamal M, et al. Common complications of hemodialysis: A clinical review. Ibnosina Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. 2021;13(04):161-172. doi:10.4103/ijmbs.ijmbs_62_21
Tinoco J, Paiva M, Lucio K, Pinheiro R, Macedo B, Lira A. Complications In Patients With Chronic Renal Failure Undergoing Hemodialysis. Cogitare Enferm. 2017;22(4):1-8. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5380/ce.v22i4.52907
Singh M, Srinivas Nayak SP, Tiwari P, Shaikh S, Gautam V, Waman Ghatol P. Review article on hemodialysis and its complications. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development. 2023;11(2):60-64. doi:10.22270/ajprd.v11i2.1236
Sánchez DG, Santos J. Symptom Burden, Comorbidity and Functional Status of patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 managed conservately. Enfermeria Global. 2021;20(3):44-54. doi:10.6018/eglobal.449531
Amini F, Oktora SI. Comorbid of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients who undergoing dialysis in Indonesia using firth logistic regression. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2021;2331:1-8. doi:10.1063/5.0041667
Marin JG, Beresford L, Lo C, Pai A, Espino-Hernandez G, Beaulieu M. Prescription Patterns in Dialysis Patients: Differences Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Patients and Opportunities for Deprescription. Canadian Journal of Kidney Health and Disease. 2020;7:1-10. doi:10.1177/2054358120912652
Pasangka IT, Tjitrosantoso H, Lolo A. Identifikasi Potensi Interaksi Obat Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Rawat Inap Di RSUP Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado. Ilmiah Farmasi. 2017;6(4):119-129.
Kimura H, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Rhee CM, Streja E, Sy J. Polypharmacy and Frailty among Hemodialysis Patients. Nephron. 2021;145(6):624-632. doi:10.1159/000516532
Colombijn JMT, Colombijn F, van Berkom L, et al. Polypharmacy and Quality of Life Among Dialysis Patients: A Qualitative Study. Kidney Medicine. 2024;6(1):1-10. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100749
Céspedes AP, Morales AJ, Bayo MP, Martínez FM, Hernández MÁM. Medication Review with Follow-Up for End-Stage Renal Disease: Drug-Related Problems and Negative Outcomes Associated with Medication—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023;12(15):1-16. doi:10.3390/jcm12155080
Luntungan P, Tjitrosantoso H, Yamlean PVY. Potensi Drug Related Problem (DRPs) Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal di Rawat Inap RSUP Prof.DR.R.D.Kandau Manado. PHARMACON Jurnal Ilmiah Farmasi. 2016;5(3):23-33.
Adibe MO, Igboeli NU, Ukwe C V. Evaluation of drug therapy problems among renal patients receiving care in some tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2017;16(3):697-704. doi:10.4314/tjpr.v16i3.27
Sakthirajan R, Varghese S, S R, P SL, M. J MS, Ramalakshmi S. Identification of Drug Related Problems among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients in A Tertiary Care Hospital. Saudi Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2019;05(11):949-955. doi:10.36348/sjmps.2019.v05i11.005
Diputra AA, Sari IP, Aries Nurulita N. Analisa Drug Related Problems (DRPS) Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik Stadium Akhir Yang Menjalani Hemodialisa Di RSUD 45 Kuningan. Journal of Pharmacopolium. 2020;3(3):107-120.
Helmy N, Kamal A, Sadek E, El minshawy O, Wahsh E. Role of clinical pharmacist in identification and resolution of drug-related problems in hemodialysis patients. Journal of advanced Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2022;5(2):96-100. doi:10.21608/jabps.2022.119078.1148
Céspedes AP, Morales AJ, Moyano AP, Bayo MP, Martínez FM, Hernández MÁM. Factors Contributing to Negative Outcomes Associated with Medications and Drug-Related Problems in Kidney Replacement Therapy—A Hospital-Based Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024;13(4):1-13. doi:10.3390/jcm13041048
Acharya S, Ragam AS, Holla R, Bhat Y ARA. Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Care Hospital: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Young Pharmacists. 2019;11(2):197-201. doi:10.5530/jyp.2019.11.41
Stefani M, Singer RF, Roberts DM. How to adjust drug doses in chronic kidney disease. Australian Prescriber. 2019;42(5):163-167. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2019.054
Hendyatama TH, Mardiana N. Calculation of Drug Dosage In Chronic Kidney Disease. Current Internal Medicine Research and Practice Surabaya Journal. 2020;1(1):21. doi:10.20473/cimrj.v1i1.16894
Loho I, Rambert G, Wowor M. Gambaran Kadar Ureum Serum pada Pasien Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Stadium 5 Non Dialisis. Jurnal e-Biomedik. 2016;4(2):2-7.
Suryaningsih NPA, Arimbawa PE, Wintariani NP, Apsari DP. Analysis of Drug Related Problems (DRPs) Of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Inpatients in a Hospital in Bali. Jurnal Ilmiah Medicamento. 2019;5(2):76-81.
Andriani S, Rahmawati F, Andayani TM. Penyesuaian Dosis Obat pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronis Rawat Inap di Rumah Sakit Kabupaten Tegal, Indonesia. Majalah Farmaseutik. 2021;17(1):46-53. doi:10.22146/farmaseutik.v17i1.48683
Spanakis M, Roubedaki M, Tzanakis I, Zografakis-Sfakianakis M, Patelarou E, Patelarou A. Impact of adverse drug reactions in patients with end stage renal disease in Greece. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020;17(23):1-18. doi:10.3390/ijerph17239101
Khusfiani T, Soetikno V, Hustrini NM, Nafrialdi. Evaluation of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions and Association with Adverse Drug Reactions in Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients at Indonesian National Referral Hospital. Acta Medica Indonesiana. 2023;55(3):277-284.
Hidayati NR, Susilo R, Anggraeni M. Kajian Potensi Interaksi Obat pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Rawat Jalan RS “X” Kota Cirebon. Pharmacon: Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia. 2020;17(2):157-164. doi:10.23917/pharmacon.v17i2.12948
Ramadaniati HU, Anggriani Y, Wowor VM, Rianti A. Drug-related problems in chronic kidneys disease patients in an Indonesian hospital: Do the problems really matter? International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016;8(12):298-302. doi:10.22159/ijpps.2016v8i12.15193
Onyedikachi EA, Ogochukwu AM, Chinwendu AK. Evaluation of Drug-Drug Interactions Among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients of Nephrology Unit in the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Ituku-Ozalla, Enugu State. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy. 2017;8(0):49-53.
Charles F, Lora L, Morton P. Drug Information Handbook. 22nd ed. Lexi Comp; 2013.
Micromedex.com. Drug Interactions.
Medscape. Drug Interaction Checker.
Baxter K. Stockley’s Drug Interactions. Ninth edit. Pharmaceutical Press; 2010.
Tatro D. Drug Interaction Facts 2013: The Authority on Drug Interactions. Wolters Kluwer Health/Facts & Comparisons; 2013.
Chaudhari ST, Sadavarte A V., Chafekar D. Clinical Profile of End Stage Renal Disease in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. MVP Journal of Medical Sciences. 2017;4(1):8. doi:10.18311/mvpjms/0/v0/i0/8555
Zafar R, Ur Rehman I, Shah Y, Ming LC, Goh HP, Goh KW. Comparative analysis of potential drug-drug interactions in a public and private hospital among chronic kidney disease patients in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: A retrospective crosssectional study. PLoS ONE. 2023;18(9 September):1-13. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0291417
Paczek B, Mucha K, Paczek L. Age-related decline in renal blood flow could be a beneficial and compensatory mechanism. Medical Science Monitor. 2020;26:2019-2021. doi:10.12659/MSM.918643
Burgh AC, Rizopoulos D, Ikram MA, Hoorn EJ, Chaker L. Determinants of the Evolution of Kidney Function With Age. Kidney International Reports. 2021;6(12):3054-3063. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.006
PERNEFRI. 11th Report Of Indonesian Renal Registry 2018. Perkumpulan Nefrologi Indonesia (PERNEFRI). Published online 2018:1-46.
Zafar W, Arshad H, Hassn R, Faqooq U, Fatima T, Rehman AU. Utilization Review of Antibiotics in the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences. 2022;16(7):196-198. doi:10.53350/pjmhs22168196
Ahmed SB, Dumanski SM. Do Sex and Gender Matter in Kidney and Cardiovascular Disease? American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2021;78(2):177-179. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.05.002
Posada I, Bobadilla NA. Understanding the opposite effects of sex hormones in mediating renal injury. Nephrology. 2021;26(3):217-226. doi:10.1111/nep.13806
Purbayanti D. Efek Konsumsi Minuman Beralkohol terhadap Kadar Kreatinin. Jurnal Surya Medika. 2018;4(1):44-50. doi:10.33084/jsm.v4i1.349
Nurul Azizah H, Argadireja DS, Susanti Armandha Y. Hubungan antara Konsumsi Alkohol dengan Kejadian Penyakit Ginjal Kronis di Instalasi Penyakit Dalam di RS Annisa Medical Center Tahun 2018. Prosiding Kedokteran. 2020;Vol. 6(1):1-5.
Setyawan Y. Merokok dan Gangguan Fungsi Ginjal. e-CliniC. 2021;9(2):388. doi:10.35790/ecl.v9i2.33991
Ariga S. Hubungan Antara Tingkat Pendidikan dan Tingkat Pengetahuan dengan Perilaku Hidup Sehat , Berkualitas di Lingkungan Rumah. Edu Society: Jurnal Pendidikan, Ilmu Sosial, dan Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat. 2022;2(3):723-730.
Hasanah U, Dewi NR, Ludiana L, Pakarti AT, Inayati A. Analisis Faktor-Faktor Risiko Terjadinya Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Pada Pasien Hemodialisis. Jurnal Wacana Kesehatan. 2023;8(2):96. doi:10.52822/jwk.v8i2.531
Natalia S, Suangga F, Pramadhani W, Isnaini. Hubungan antara lama menjalani hemodialisa dengan kualitas hidup pasien gagal ginjal kronik di ruang hemodialisa di salah satu rsud di batam. An-Najat : Jurnal Ilmu Farmasi dan Kesehatan. 2023;1(2):108-115.
Madania M, Tuloli TS, Rasdianah N, Akuba J. Analisis Biaya dan Nilai Utilitas pada Pasien Hemodialisis yang Diberikan Terapi Erythropoiesis di Rumah Sakit. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 2022;1(3):190-202. doi:10.37311/ijpe.v1i3.11360
Ratnasari PMD, Yuliawati AN, Dhrik M, Cahyadi KD. Hubungan Pengetahuan terhadap Kepatuhan Pengobatan Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik yang Menjalani Hemodialisis. Jurnal Ilmu Farmasi dan Farmasi Klinik. 2023;20(2):144. doi:10.31942/jiffk.v20i2.8379
Kamaliah N, Cahaya N, Rahmah S. Gambaran Karakteristik Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik Yang Menggunakan Suplemen Kalsium di Poliklinik Sub Spesialis Ginjal Hipertensi Rawat Jalan RSUD Ulin Banjarmasin. Jurnal Pharmascience,. 2021;08(01):111-124.
Amalia A, Apriliani N. Analisis Efektivitas Single Use dan Reuse Dialyzer pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik di RSUD Mardi Waluyo Kota Blitar. Iurnal Sains dan Kesehatan. 2021;3(5):679-686. doi:10.24293/ijcpml.v13i3.910
Mahato SKS, Apidechkul T, Sriwongpan P, et al. Factors associated with quality of life among chronic kidney disease patients in Nepal: A cross-sectional study. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):1-14.
Polanska B, Uchmanowicz I, Wysocka A, Uchmanowicz B, Lomper K, Fal AM. Factors affecting the quality of life of chronic dialysis patients. European Journal of Public Health. 2017;27(2):262-267. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckw193
Wells B, Dipiro J, Dipiro C, Schwinghammer T. Pharmacotherapy Handbook. Ninth Edit.; 2019.
Agarwal R. Mechanisms and mediators of hypertension induced by erythropoietin and related molecules. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2018;33(10):1690-1698. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfx324
Artiany S, Gamayana Trimawang Aji Y. Gambaran Komorbid pada Pasien Hemodialisis di Rumah Sakit Angkatan Udara (RSAU) drEsnawan Antariksa. Jurnal Keperawatan Cikini. 2021;2(2):1-6. doi:10.55644/jkc.v2i2.57
Abdulhadi MG, Mohammed M, Maarouf FB. Dyslipidemia among Patients with End Stage Renal Disease on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research. Published online 2018:123-128. doi:10.24017/science.2018.2.20
Fatima A, Anwar S, Awan A, Ahmad S, Usman H, Anwar Z. Frequency of Restless Legs Syndrome among End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Medical Forum Monthly. 2022;33(2):138-141.
Hanyaq A, Ramadhan, AM. Samsul E. Kajian Interaksi Obat Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronis Di Instalasi Rawat Inap Rumah Sakit Samarinda Medika Citra. Proceeding of Mulawarman Pharmaceuticals Conferences. Published online 2021:135-138. doi:https://doi.org/10.25026/mpc.v14i1.598 1
Pinzon RT, Ardiani BL. Benefit administration of vitamin B1, B6, and B12 on the depression symptom in hemodialysis patients. Farmasains : Jurnal Farmasi dan Ilmu Kesehatan. 2020;4(2):7-13. doi:10.22219/farmasains.v4i2.8919
Sadjadi SA, Pi A. Hyperphosphatemia, a cause of high anion gap metabolic acidosis: Report of a case and review of the literature. American Journal of Case Reports. 2017;18:463-466. doi:10.12659/AJCR.902862
Iwashita Y, Ohya M, Kunimoto S, et al. A survey of drug burden in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis in Japan. Internal Medicine. 2018;57(20):2937-2944. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.0108-17
Ariani N, Prihandiwati E. Evaluasi Potensi Interaksi Obat Antidiabetika Oral Di Apotek Perintis Kuripan Banjarmasin. Jurnal Insan Farmasi Indonesia. 2021;4(2):301-308. doi:10.36387/jifi.v4i2.821
Nurjanah F, Sriwidodo S, Nurhadi B. Stabilisasi Tablet yang Mengandung Zat Aktif Bersifat Higroskopis. Majalah Farmasetika. 2020;6(1):10. doi:10.24198/mfarmasetika.v6i1.27420
Hassan Z, Ali I, Ullah AR, et al. Assessment of Medication Dosage Adjustment in Hospitalized Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. Cureus. 2021;13(2):1-10. doi:10.7759/cureus.13449
Haryati N, Rahmawati F, Wahyono D. Penyesuaian Dosis Obat Berdasarkan Nilai Kreatinin Klirens pada Pasien Geriatri Rawat Inap di Rsup Dr. Kariadi Semarang, Indonesia. Majalah Farmaseutik. 2019;15(2):75. doi:10.22146/farmaseutik.v15i2.46447
Tuloli TS, Madania M, Mustapa MA, Tuli EP. Evaluasi Penggunaan Obat Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik Yang Menjalani Hemodialisis Di Rsud Toto Kabila Periode 2017-2018. Parapemikir : Jurnal Ilmiah Farmasi. 2019;8(2):25. doi:10.30591/pjif.v8i2.1470
Pradiningsih A, Nopitasari B, Wahyuningsih E. Evaluasi Penggunaan Obat Antihipertensi pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik Rawat Inap di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Barat. Lumbung Farmasi Jurnal Ilmu Kefarmasian. 2020;1(2):61-70.
Farnoud M, Mehrpooya M, Mahboobian MM, Mohammadi Y, Mohammadi M. Evaluation of drug-drug interactions in chronic kidney disease patients: A single-center experience. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020;16(4):81-92.
Hammoud KM, Sridhar SB, Rabbani SA, Kurian MT. Evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions among chronic kidney disease patients: An experience from United Arab Emirates. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2022;21(4):853-861. doi:10.4314/tjpr.v21i4.24
Okoro RN, Ummate I, Ohieku JD, Yakubu SI, Adibe MO, Okonta MJ. Kidney Disease Knowledge and Its Determinants Among Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Patient Experience. 2020;7(6):1303-1309. doi:10.1177/2374373520967800
Shahzadi A, Sonmez I, Kose C, et al. The Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions in CKD-A Retrospective Observational Study of Cerrahpasa Nephrology Unit. Medicina (Lithuania). 2022;58(2):1-10. doi:10.3390/medicina58020183
Makmur SA, Madania M, Rasdianah N. Gambaran Interaksi Obat Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronik Dalam Proses Hemodialisis. Indonesian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. 2022;2(3):218-229. doi:10.37311/ijpe.v2i2.13333
Berg JPV., Vereecke HEM, Proost JH, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions in anaesthesia. A review of current knowledge and how it can be used to optimize anaesthetic drug administration. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2017;118(1):44-57. doi:10.1093/bja/aew312
Rengga MPE, Kono RB, Beama CA. Analisis Interaksi Obat Penyakit Ginjal Kronik di RSUD Prof. Dr. W. Z. Johannes Kupang. MPI (Media Pharmaceutica Indonesiana). 2021;3(3):179-187. doi:10.24123/mpi.v3i3.3937
Nusair MB, Al-Azzam SI, Arabyat RM, Amawi HA, Alzoubi KH, Rabah AA. The prevalence and severity of potential drug-drug interactions among adult polypharmacy patients at outpatient clinics in Jordan. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2020;28(2):155-160. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.009
Al-Ramahi R, Raddad AR, Rashed AO, et al. Evaluation of potential drug- drug interactions among Palestinian hemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrology. 2016;17(1):1-6. doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0317-4
Chaudhary SK, Manadhar N, Adhikari L. Polypharmacy and potential drug-drug interactions among medications prescribed to chronic kidney disease patients. Janaki Medical College Journal of Medical Science. 2021;9(1):25-32. doi:10.3126/jmcjms.v9i1.38047
Anggriani A, Kusumahati E, Mutazam IH. Potensi Interaksi Obat Amlodipin Pada Pasien Hipertensi Disalah Satu Puskesmas Kabupaten Sumedang. Jurnal Riset Kefarmasian Indonesia. 2021;3(1):1-9. doi:10.33759/jrki.v3i1.108
Sayem AS, Arya A, Karimian H, Krishnasamy N, Hasamnis AA, Hossain CF. Action of phytochemicals on insulin signaling pathways accelerating glucose transporter (GLUT4) protein translocation. Molecules. 2018;23(2):1-15. doi:10.3390/molecules23020258
Divakaran S, Loscaizo J. The Role of Nitroglycerin and Other Nitrogen Oxides in Cardiovascular Therapeutics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;70(19):2393-2410. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.1064.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Pande Made Desy Ratnasari, Mahadri Dhrik, Laili Kurnia Rizqy Rizqy, Ni Kadek Dwi Rosita Devi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





















