The Relationship Between Demographics and Knowledge of Traditional Medicine Use: A Study of the Banjar X Community, Gianyar Regency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/usadha.v4i3.13134Keywords:
demographics, traditional medicine, community, knowledgeAbstract
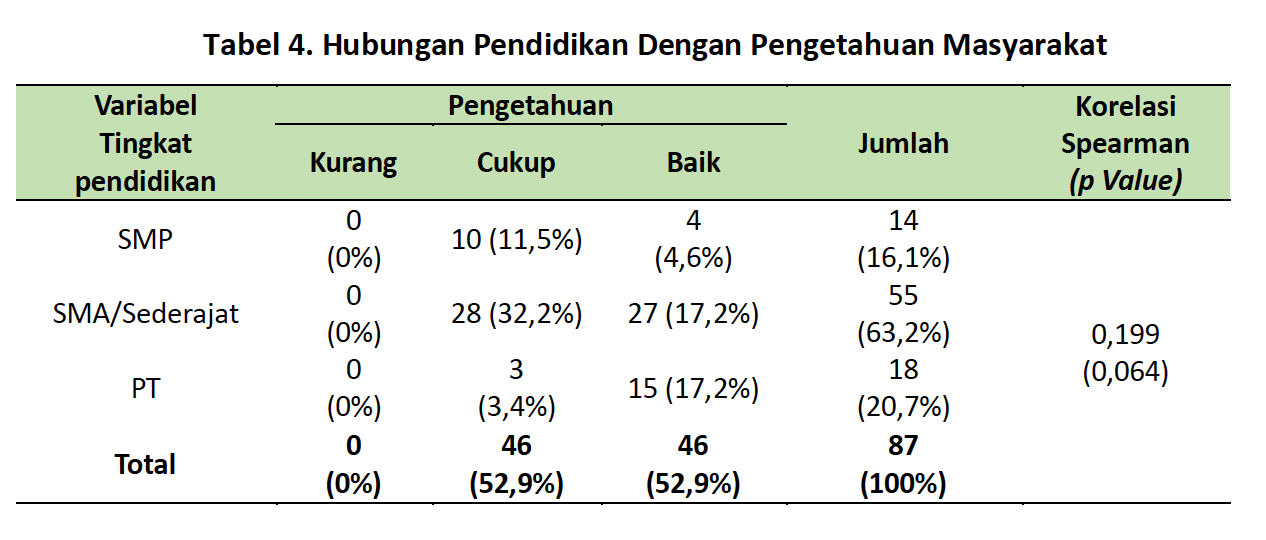
The use of traditional medicine in the modern era is gaining popularity, as it is often considered to have fewer side effects compared to modern medicine. Traditional remedies have been used for generations by communities as an alternative approach to maintaining health. This study aims to assess the level of community knowledge and to analyze the relationship between demographic factors (age, gender, education, occupation, and income) and knowledge regarding the use of traditional medicine. A descriptive-analytic design was employed, with data collected through door-to-door questionnaires. The study was conducted in Banjar X, Gianyar Regency, with a population of 619 households. A total of 87 respondents were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The findings revealed that the community’s level of knowledge was categorized as good (52.9%). Analysis of demographic factors and knowledge indicated associations between age (p = 0.079), income (p = 0.076), and education (p = 0.064) with knowledge of traditional medicine use. Thus, certain demographic characteristics—namely age, education, and income—were found to be significantly related to the level of community knowledge in using traditional medicine in Banjar X. These results highlight the important role of demographic factors in shaping public health literacy concerning traditional medicine.
References
[1]. Parwata IMOA. Obat Tradisional. Jurnal Keperawatan Universitas Jambi. 2016;218799.
[2]. Azizah AN, Kurniati CH. Obat Herbal Tradisional Pereda Batuk Pilek Pada Balita. Jurnal Kebidanan Indonesia. 2020;11(2):29.
[3]. Anonim. PROFIL DESA LEBIH. 2021.
[4]. Afriliana. Gambaran Pengetahuan dan Sikap Masyarakat Terhadap Penggunaan Obat Tradisional Dikecamatan Mlati. Universitas Islam Indonesia. 2019;1–72.
[5]. Yuhara NA, Rawar EA, Admaja SP. Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Masyarakat Terhadap Penggunaan Obat Tradisional Herbal Dalam Pencegahan Covid-19. Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat. 2020;(November):385–92.
[6]. Darsini D, Fahrurrozi F, Cahyono EA. Pengetahuan; Artikel Review. Jurnal Keperawatan. 2019;12(1):13.
[7]. Sugiyono. Metode Penelitian Kualitatif, Kuantitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta Bandung. 2019.
[8]. Meithia A. Peningkatan Literasi Kesehatan Berbasis Tanaman Obat Keluarga melalui Pelatihan Pembuatan Jamu pada Pendidikan Kesetaraan. Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat Farmasi : Pharmacare Society [Internet]. 2025 Sep 12;4(3):192–200. Available from: https://ejurnal.ung.ac.id/index.php/Jpmf/article/view/34031
[9]. Reiza Adiyasa M. Pemanfaatan obat tradisional di Indonesia: distribusi dan faktor demografis yang berpengaruh. Jurnal Biomedika dan Kesehatan [Internet]. 2021;4(3).
[10]. Desni F, Agung Wibowo T, Rosyidah. Hubungan Pengetahuan, Sikap, Perilaku Kepala Keluarga Dengan Pengambilan Keputusan Pengobatan Tradisional Di Desa Rambah Tengah Hilir Kecamatan Rambah Kabupaten Rokan Hulu, Riau. 2021.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fitria Megawati, Ni Luh Kade Arman Anita Dewi, Ni Luh Firda Ekayanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




