Narrative Review: Cost Effectiveness of Using Antibiotics for Pneumonia in Indonesian Hospitals
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/medicamento.v9i2.4827Keywords:
antibiotic, pneumonia, cost effectiveAbstract
Pneumonia is an acute inflammatory respiratory infection caused by microorganisms. This infection can occur from both toddlers to the elderly and if not properly then the acute respiratory inflammation process will continue to be able to cause various infectious complications. Until now, there are many choices of antibiotic therapy for their treatment, but they have not guaranteed their effectiveness both therapeutically and cost-effectively. The purpose of this study was to analyze the effectiveness and efficiency of pneumonia treatment costs in Indonesian Hospitals. The method used is a literature review approach, namely Systematic Review related to articles with cost-effectiveness analysis or Cost-effectiveness analysis of pneumonia treatment that have been published in the form of research articles. Search articles using three databases, namely Google Scholar, Pubmed, and Garudadekti. Then the selection stage or literature screening was carried out by reading the title, abstract, and continued with the full text of the research article obtained. The results obtained 14 research articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria regarding the cost-effectiveness of pneumonia treatment. From the research data, it can be concluded that the antibiotic cefotaxime is widely prescribed and the most cost-effective according to the ACER calculation. However, the ACER value is influenced by different drug administration for each patient, the effectiveness of treatment therapy, the costs incurred by the patient or direct medical costs.
References
Andayani, T.M. (2013). Farmakoekonomi : Prinsip dan Metodologi. Bursa Ilmu, Yogyakarta.
Azmi, S., Aljunid, S.M., Maimaiti, N., Ali, A.A., Muhammad, A., De Rosas-Valera M. (2016). Assessing The Burden of Pneumonia Using Administrative Data From Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines. Int J Infect Dis, 49, :87–93. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.20 16.05.021
Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar (RISKESDAS) 2013. Laporan Nasional 2013, 46, 1–384. https://doi.org/1 Desember 2013
Bakhri, S. (2018). Analisis Jumlah Leukosit Dan Jenis Leukosit Pada Individu Yang Tidur Dengan Lampu Menyala Dan Yang Dipadamkan. Jurnal Media Analis Kesehatan, 1(1), 83–91. https://doi.org/10.32382/mak.v1i1.176
Bartolf, A., Cosgrove C. (2016). Pneumonia. Medicine (Baltimore), 44(6), 373– 7. doi: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2016.03.004
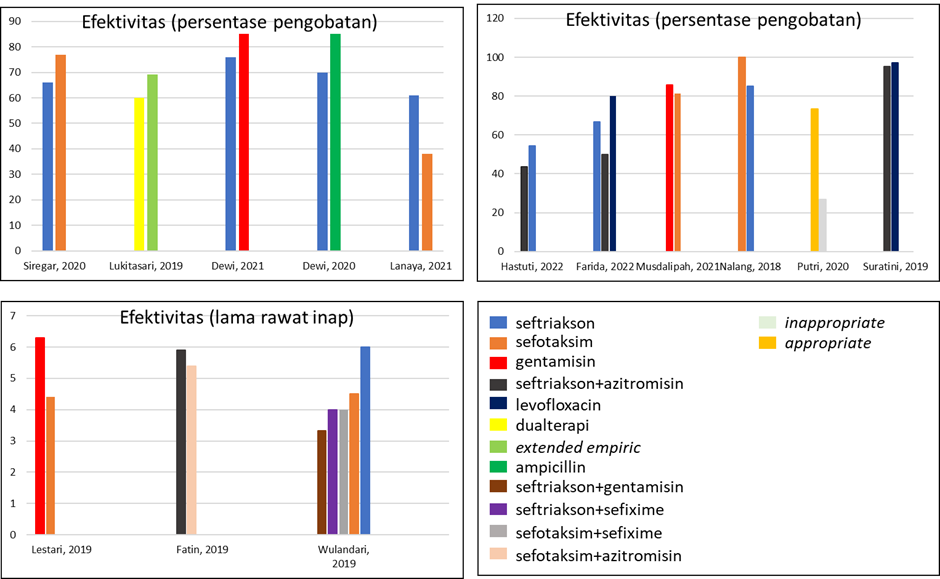
Dewi, R., Andriani, M., Oktaviazmi, S.P. (2021). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Penggunaan Antibiotik Ceftriaxone dan Gentamisin pada Pasien Pneumonia Anak Rawat Inap Rumah Sakit X di Jambi Tahun 2018. Pharma Xplore, 6(1), 43-51.
Dewi, R., Sanuddin, M., Shaleha., M. (2020). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Penggunaan Antibiotik Ceftriaxone dan Ampicilin pada Pasien Pneumonia Anak Rawat Inap di RSUD Raden Mattaher Jambi tahun 2018. Journal of Healthcare Technology and Medicine, 6(2), 616-625.
Eljaaly, K., Alshehri, S., Aljabri, A., Abraham, I., Al Mohajer, M., Kalil, A.C. (2019). Clinical Failure With And Without Empiric Atypical Bacteria Coverage In Hospitalized Adults With Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Systematic Review And Meta– Analysis. BMC Infect Dis, 17,385.
Fa’idha, A.F., Mufida, D.C., Febianti, Z. (2020). Peran Protein Hemaglutinin Pili Streptococcus Pneumoniae 54 Kda Sebagai Adhesin. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan (Journal Of Health Science). 13(2), 194-205.
Farida, Y., Khoiry, Q.A., Hanafi, M., Maryani. (2022). Cost-Effectiveness Analysis Of Empiric Antibiotics In Hospitalized Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Pharmaciana, 12(1), 83-93.
Fatin, M.N.A., Rahayu, C., Suwantika, A.A. (2019). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Penggunaan Antibiotik pada Pasien Community-acquired Pneumonia di RSUP Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung. Jurnal Farmasi Klinik Indonesia, 8(3), 228-236.
Hastuti, S., Islam, Z., Amaliah, A., Ruskar, D. (2022). Perbandingan Analisis Biaya Penggunaan Antibiotik Seftriakson Tunggal Dengan Kombinasi Antibiotik Lain Pada Pasien Pneumonia Komunitas. PENDIPA Journal of Science Education, 6(2), 394-403.
Hulscher, M.E.J.L., Grol, R.P.T.M., Meer, J.W.M, Van Der. (2010). Antibiotic Prescribing in Hospitals : A Social and Behavioural Scientific Approach. Lancet Infect Dis, 10, 165–75.
Irawan, R., Reviono., Harsini.(2019). Korelasi Kadar Copeptin dan Skor PSI dengan Waktu Terapi Sulih Antibiotik Intravena ke Oral dan Lama Rawat Pneumonia Komunitas. J Respir Indo, 39(1),44-57.
Khoiriyah, S.D., dan Lestari, K.(2018). Review Artikel: Kajian Farmakoekonomi yang Mendasari Pemilihan Pengobatan di Indonesia. Farmaka, 16(3), 134-145.
Kementrian Kesehatan RI. (2017). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2017. Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Lanaya, D., Anggraini, Y., Sarnianto, P. (2021). Efektivitas Biaya Antibiotik Seftriakson dan Sefotaxim dalam Pengobatan Pneumonia. Jurnal Kesehatan Poltekkes Kemenkes RI Pangkalpinang, 9(2), 101-111.
Lestari, M.D., Citraningtyas, G., Edy, H.J. (2019). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Pasien Pneumonia Balita Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Bhayangkara Manado. Pharmacon, 8(4), 968-976.
Lee, M. S., Oh, J. Y., Kang, C. I., Kim, E. S., Park, S., Rhee, C. K., Jung, J.Y., Jo, K.W., Heo, E.Y., Park, D.A. and Kiem, S. (2018). Guideline for Antibiotik Use in Adults with Community-acquired Pneumonia. Infection & Chemotherapy, 50(2), 160–198.
Lukitasari, N., Radji, M., Rianti, A. (2019). Analisis Perbandingan Antara Monoterapi dengan Dualterapi Antibiotik Extended Empiric pada Pasien Community-Acquired Pneumonia di RSUP Fatmawati Jakarta. Jurnal Sains Farmasi & Klinis, 6(2), 147-157.
Mattila, J.T., Fine, M.J., Limper, A.H., Murray, P.R., Chen, B.B., Lin, P.L. (2014). Pneumonia: Treatment and Diagnosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc,11, 189-92.
Munguia, J. I., L., Pulzová, K. Bhide, Ľ., Čomor, E., Káňová, Z., Tomečková, I. Širochmanová, M., Bhide. (2018). Contribution of Pili of S. pneumoniae in the Onset of Meningitis. Folia Veterinaria, 62(1), 67–72.
Musdalipah., Setiawan, M.A., Santi, E. (2021). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Antibiotik Sefotaxime dan Gentamisin Penderita Pneumonia pada Balita fi RSUD Kabupaten Bombana Provinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Jurnal Ilmiah Ibnu Sina, 3(1), 1-11.
Musher, D.M., Abers, M.S., and Bartlett, J.G.(2018). Evolving Understanding of the Causes of Pneumonia in Adults, With Special Attention to the Role of Pneumococcus. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 15(9), 1736-1745.
Nalang, A, Citraningtyas., Lolo, W.A. (2018). Analisis efektivitas biaya (cost effectiveness analysis) pengobatan pneumonia menggunakan antibiotik seftriakson dan sefotaksim di RSUP Prof. Dr. RD Kandou Manado. Pharmacon, 7(3), 321-330.
Nie, W., Li, B., Xiu, Q.(2014). β-Lactam/Macrolide Dual Therapy Versus Β-Lactam Monotherapy for the Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother, 69(6), 1441–1446. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku 033
Osman, M., Manosuthi, W., Kaewkungwal, J., Silachamroon, U., Mansanguan, C. (2021). Etiology, Clinical Course, and Outcomes of Pneumonia in the Elderly: A Retrospective and Prospective Cohort Study in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg, 106(6), 1-8.
PDPI. (2020). Press Release “Perhimpunan Dokter Paru Indonesia (PDPI) Outbreak Pneumonia di Tiongkok. Perhimpunan Dokter Paru Indonesia
PDPI. (2014). Pneumonia Kominitas Pedoman Diagnosis & Penatalaksanaan di Indonesia. Perhimpunan Dokter Paru Indonesia.
Putri, I.S., Hapsari, R., Ciptaningtyas, V.R. (2020). Appropriate Usage of Antibiotics and Its Cost-Effectiveness. Diponegoro Medical Journal, 9(6), 448-452.Lieberman, J.A.Y.M. (2003). Appropriate Antibiotic Use and Why It Is Important : The Challenges of Bacterial. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 22(12). 1143–1151.
Raini, M. (2016). Antibiotik Golongan Fluorokuinolon: Manfaat dan Kerugian Fluoroquinolones Antibiotiks: Benefit and Side Effects. Media Litbangkes, 26(3), 163– 174.
Ramirez, J., Wiemken, T., Peyrani, P., Arnold, F., Kelley, R., Mattingly, W., Nakamatsu, R., Pena, S., Guinn, B., Furmanek, Persaud, A., Raghuram, A., F, F., L, (2017). Adults Hospitalized With Pneumonia in the United States: Incidence, Epidemiology, and Mortality. Clinical Infectious Diseases : An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 65(11), 1806–1812. https://doi.org/10.1093/CID/CIX647
Rusmini, H. (2016). Gambaran Penggunaan Antibiotik Pada Pasien Pneumonia Dengan Menggunakan Metode Gyssens Di Rawat Inap Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah (RSUD) H. Abdul Moeloek Tahun 2015. Jurnal Medika Malahayati, 3(2), 61–64. https://doi.org/10.33024/jmm.v3i2.2009
Selçuk, A.A. (2019). A Guide for Systematic Reviews: PRISMA. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 57(1):57-8. doi: 0.5152/tao.2019.4058, PMID 31049257.22
Setiawan, D., Endarti, D., & Suwantika, A. (2017). Farmakoekonomi modeling. Purwokerto. UM Purwokerto Press
Siregar, H.N., Prabowo, I., Hadiwiardjo, Y.H. (2020). Analisis Efektivitas Biaya Penggunaan Antibiotik Seftriakson dan Sefotaksim pada Pasien Pneumonia Komunitas Bayi dan Balita di Instalasi Rawat Inap RSUP Fatmawati Tahun 2017- 2018. Seminar Nasional Riset Kedokteran, 112-122.
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature Review As A Research Methodology: An Overview And Guidelines. J Bus Res, 104, 333-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039.jbusres.2019.07.039.
Smith, M., Fee, C., Mace, S., Maughan, B., Perkins, J., Kaji, A., & Wolf, S. (2021). Clinical Policy: Critical Issues in the Management of Adult Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 77(1), 41–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2020.10.024
Sumiyati. (2015). Hubungan Jenis Kelamin Status Imunisasi DPT Dengan Pneumonia Bayi Usia 0-12 Bulan. Jurnal Kesehatan Metro Sai Wawai, 8(2), 63 – 69
Suratini, S., Sauriasari, R., Hamadah, F., Kusumaeni, T. (2019). Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Ceftriaxone-Azithromycin Combination and Single Levofloxacin As Empirical Antibiotics in Community-Acquired Pneumonia Inpatients at Persahabatan Hospital. Asian J Pharm Clin Res, 10(2), 1-6.
Takahashi, K., Suzuki, M., Minh, L. N., Anh, N. H., Huong, L. T. M., Son, T. V. V., Long, P. T., Ai, N. T. T., Tho, L. H., Morimoto, K., Kilgore, P. E., Anh, D. D., Ariyoshi, K., & Yoshida, L. M. (2013). The incidence and Aetiology of Hospitalised Community-Acquired Pneumonia Among Vietnamese Adults: A Prospective Surveillance in Central Vietnam. BMC Infectious Diseases, 13(1).
Thanassi, D. G., J. B. Bliska, dan P. J. Christie. (2012). Surface Organelles Assembled by Secretion Systems of Gram Negative Bacteria: Diversity in Structure and Function. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 36(6), 1046–1082.
Wahidah, L. M., Wayuni, N.T., Putri, D.M. (2020). Evaluasi Penggunaan Antibiotik Pneumonia dengan Metode ATC/DDD pada Pasien Pediatri di Instalasi Rawat Inap RSUD DR. A Dadi Tjokrodipo Bandar Lampung Tahun 2019. Jurnal Farmasi Lampung. 9(2), 1-15.
Wildan, M., Husin, U.A., Roekmantara. (2018). Perbandingan Efektivitas Penggunaan Ceftriaxone dengan Cefotaxime pada pasien demam tifoid Anak Berdasarkan Lama Rawat Inap di RSUD Al-Ihsan Kebupaten Bandung 2016-2017. Bandung: Prosiding Pendidikan Dokter.
Wo´jkowska-Mach, J., Gryglewska, B., Romaniszyn, A., Natkaniec, J., Pobiega, M., Adamski, P., Grodzicki, T., Kubicz K., Heczko, P.B. (2013). Age and Other Risk Factors of Pneumonia Among Residents of Polish Long-Term. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 17, 37-43.
Wulandari, N.T., Listyanti, E., Dyahariesti, N., Erwiyani, A.R. (2019). Analisis Keefektifan Biaya Pengobatan Pada Pasien Pneumonia Balita Di Instalasi Rawat Inap Rumah Sakit Paru Dr. Ario Wirawan Salatiga Tahun 2018. Indonesian Journal of Pharmacy and Natural Product, 2(2), 94-108.
Downloads
Submitted
Accepted
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Jurnal Ilmiah Medicamento

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

















