The The Association of Genetic Polymorphism on the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36733/usadha.v3i3.10956Keywords:
chronic kidney disease, genetic, gene polymorphism, SNPAbstract
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is an escalating global health issue, particularly in Indonesia. CKD is characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in renal function, with diabetes mellitus and hypertension as primary risk factors. Genetic polymorphisms, variations in DNA sequences that affect gene function and protein expression, play a critical role in CKD risk and progression. This narrative review examines the role of genetic polymorphisms in CKD risk based on available literature. Scientific articles were sourced from PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, and Scopus using keywords related to genetic polymorphisms and CKD. From the 441 articles identified, selection was based on relevance, sample size, and article completeness. Several genetic polymorphisms were found to have significant associations with increased CKD risk, including Renalase (rs2296545), GSTO1 (rs2164624), GSTO2, MMP3 (rs35068180), and MGP (rs4236), among others such as CYP24A1, GPX1, UMOD, CYP2C8, CYP4A11, EPHX2, SPP1, and BGLAP. These polymorphisms influence mechanisms such as blood pressure regulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue calcification, all contributing to CKD progression. In conclusion, genetic polymorphisms are crucial in CKD risk, offering insights for more personalized approaches in diagnosing, preventing, and treating this condition. These findings support the development of more effective, genetics-based treatment strategies in the future.
References
[1] Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Laporan Nasional: RISKESDAS 2018. Jakarta, Indonesia: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan; 2019.
[2] Dipiro JT, Yee GC, Posey LM, Haines ST, Nolin TD, Ellingrod V. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach. 11th ed. McGraw Hill Medical; 2020.
[3] Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran: Tata Laksana Penyakit Ginjal Kronik 2023.
[4] Hewagama A, Richardson B. The genetics and epigenetics of autoimmune diseases. Journal of Autoimmunity 2009;33:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.03.007.
[5] Wang Y, He W. Endogenous Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 as an Antioxidant in Liver. The Liver, Elsevier; 2018, p. 247–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803951-9.00021-5.
[6] International Consortium for Blood Pressure Genome-Wide Association Studies, Ehret GB, Munroe PB, Rice KM, Bochud M, Johnson AD, et al. Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Nature 2011;478:103–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10405.
[7] Al-Ajeeli ZA, Hameed HH. The Renalase (rs2296545) Polymorphism is Associated with End-Stage Renal Disease 2024;7:16–20.
[8] Malyszko J, Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Dobrzycki S. Renalase, kidney and cardiovascular disease: are they related or just coincidentally associated? Adv Med Sci 2015;60:41–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2014.10.001.
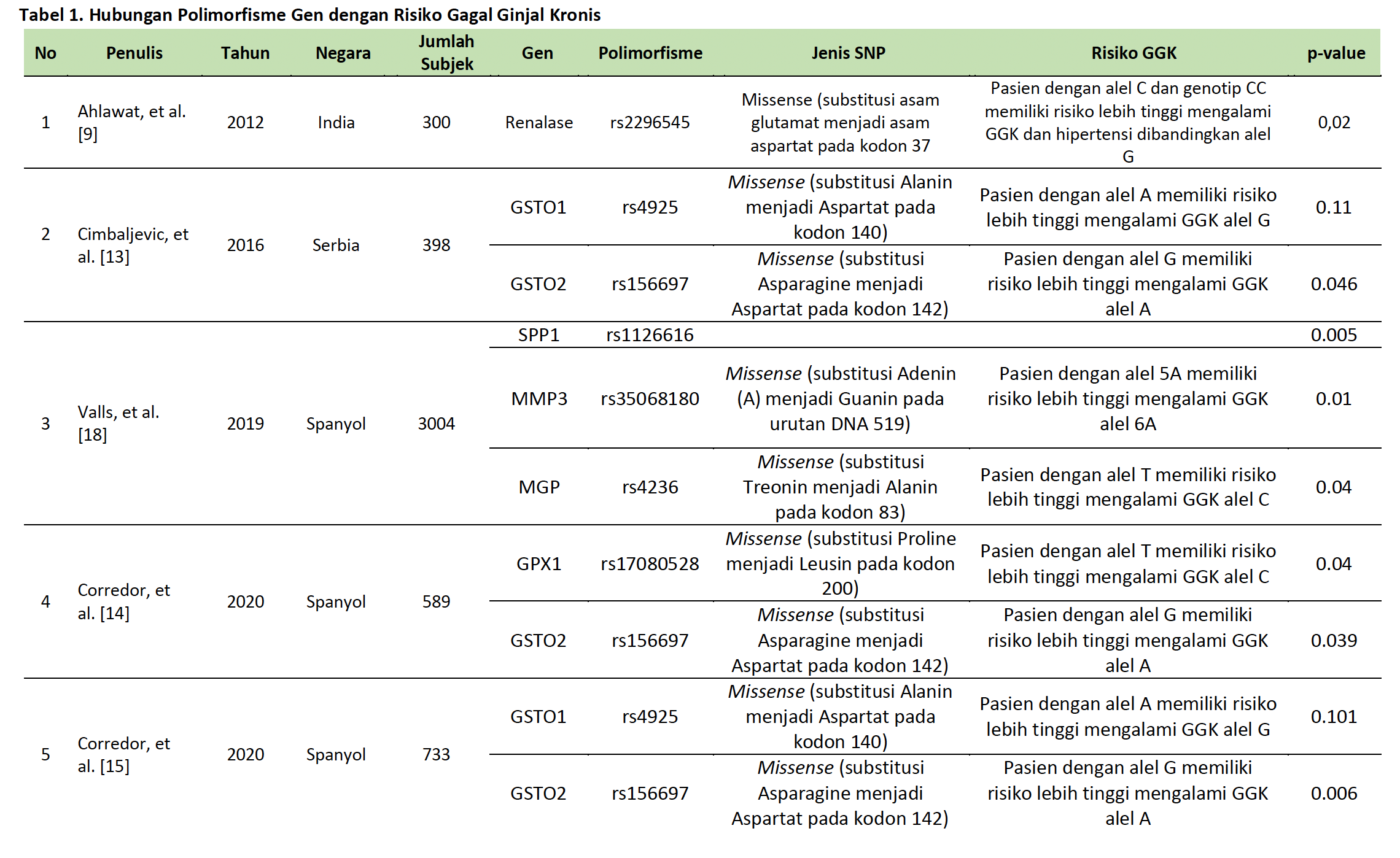
[9] Ahlawat RS, Gupta S, Kapoor S, Kar P. Polymorphism of Renalase Gene in Patients of Chronic Kidney Disease. OJNeph 2012;02:136–43. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojneph.2012.24021.
[10] Khater MH, Abd EL-Hassib DM, Sabry JH, Elkilany RM, Ameen SG. Association Between Renalase Gene Polymorphism (rs2296545) and Hypertension in Egyptian Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Cureus 2023. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.47903.
[11] Lv Y-B, Wang Y, Ma W-G, Yan D-Y, Zheng W-L, Chu C, et al. Association of Renalase SNPs rs2296545 and rs2576178 with the Risk of Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2016;11:e0158880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158880.
[12] Board PG, Menon D. Structure, function and disease relevance of Omega-class glutathione transferases. Arch Toxicol 2016;90:1049–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1691-1.
[13] Cimbaljevic S, Suvakov S, Matic M, Pljesa-Ercegovac M, Pekmezovic T, Radic T, et al. Association of GSTO1 and GSTO2 Polymorphism with Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease Development and Patient Survival. Journal of Medical Biochemistry 2016;35:302–11. https://doi.org/10.1515/jomb-2016-0009.
[14] Corredor Z, Da Silva Filho MI, Rodríguez-Ribera L, Catalano C, Hemminki K, Coll E, et al. Loci associated with genomic damage levels in chronic kidney disease patients and controls. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2020;852:503167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2020.503167.
[15] Corredor Z, Filho MIDS, Rodríguez-Ribera L, Velázquez A, Hernández A, Catalano C, et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in a Spanish Population. Sci Rep 2020;10:144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56695-2.
[16] Wan J, Zhang G, Li X, Qiu X, Ouyang J, Dai J, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase 3: A Promoting and Destabilizing Factor in the Pathogenesis of Disease and Cell Differentiation. Front Physiol 2021;12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.663978.
[17] Yamada. Association of gene polymorphisms with chronic kidney disease in high- or low-risk subjects defined by conventional risk factors. Int J Mol Med 2009;23. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm_00000193.
[18] Valls J, Cambray S, Pérez-Guallar C, Bozic M, Bermúdez-López M, Fernández E, et al. Association of Candidate Gene Polymorphisms With Chronic Kidney Disease: Results of a Case-Control Analysis in the Nefrona Cohort. Front Genet 2019;10:118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00118.
[19] Darraji M, Saqban L, Mutar T, Rasheed M, Hussein A. Association of Candidate Genes Polymorphisms in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J Adv Biotechnol Exp Ther 2022;6:687. https://doi.org/10.5455/jabet.2022.d147.
[20] Jerotic D, Matic M, Suvakov S, Vucicevic K, Damjanovic T, Savic-Radojevic A, et al. Association of Nrf2, SOD2 and GPX1 Polymorphisms with Biomarkers of Oxidative Distress and Survival in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Toxins 2019;11:431. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070431.
[21] Suárez-Santisteban MA, Santos-Díaz G, García-Bernalt V, Pérez-Pico AM, Mingorance E, Mayordomo R, et al. Association between CYP4A11 and EPHX2 genetic polymorphisms and chronic kidney disease progression in hypertensive patients. Nefrología (English Edition) 2024;44:382–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nefroe.2024.01.020
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Penulis

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




